completed Assessment
Digital Diabetes Management Solutions
Assessment Released
Last Updated
April 19, 2024
Conditions
Type 2 Diabetes
"*" indicates required fields
PHTI evaluated digital diabetes management tools that support improved glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes.
Area overview
Type 2 diabetes impacts almost one in seven people in the United States and is the most expensive chronic condition, leading to significant clinical complications. Given the critical role of patient self-management in diabetes, there has been significant investment in creating digital diabetes management solutions with patients as the primary users.
The core objective of these solutions is to support improved glycemic control through tracking of blood glucose, paired with additional education and support. These solutions use three broad approaches:
- Remote patient monitoring—Enable physicians to support remote patient monitoring of blood glucose levels with a goal of improved glycemic control.
- Behavior and lifestyle modification—Engage patients with a mix of behavioral, clinical, and lifestyle modification programs in addition to glycemic feedback with a goal of glycemic control and other health improvements.
- Nutritional ketosis—Induce a state of ketosis in patients through intensive dietary guidance and monitoring of glycemic and ketone levels with the goal of diabetes remission.
Download the evaluation

Digital Diabetes Management Solutions
Updated April 19, 2024
March 21, 2024
Executive SummaryMarch 21, 2024
Providers’ GuideMarch 21, 2024
Patient GuideMarch 21, 2024
Overview for PolicymakersMarch 28, 2024
AppendicesJanuary 21, 2026
Performance-Based Contracting ToolkitReport contributors and reviewers provided important expertise and insight throughout our process. Those who directly contributed to the report have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Webinar
Summary of findings
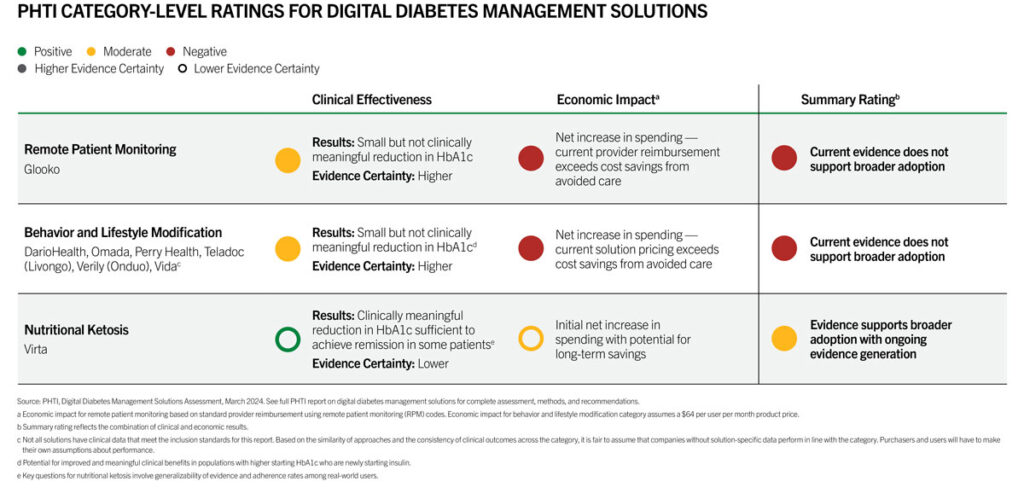
Digital diabetes tools in the remote patient monitoring and behavior and lifestyle modification categories do not deliver meaningful clinical benefits, and they increase healthcare spending relative to usual care. The evidence showed that improvements in glycemic control for patients using digital diabetes management solutions were minimal and short-term.
After accounting for the average price of these products, these solutions increase net healthcare spending for purchasers because the small, estimated savings are less than the cost of the solution. Exceptions may include 1) people with higher starting HbA1c who are newly starting insulin, and 2) people seeking diabetes remission through nutritional ketosis.
These findings are based on the criteria set forth in the ICER-PHTI Assessment Framework and the currently available evidence. PHTI conducted a secondary research review that relied on published literature and information. PHTI did not conduct original testing of the tools. Please see the full Digital Diabetes Management Solutions report for the complete assessment, methods, and recommendations.
Guidance & considerations for stakeholders
Purchasers
- Require data analysis and transparency
- Align payment for solutions with their clinical performance, including financial performance guarantees in contracts
- Focus the deployment of solutions to patients with the highest HbA1c levels
Innovators
- Clinical evidence generation is critical to support adoption
- Sustainability of clinical benefits is central to a solution’s impact
- Provider acceptance and engagement matters
- Contract for results
Providers
- Performance may vary by sub-population
- Diabetic remission is a worthy goal that may be supported with effective digital solutions
- Be aware that many digital health solutions are cost-additive
Why assess digital diabetes management tools?
- In the United States, about one in seven adults–more than 38 million Americans–have diabetes, and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes among adults is expected to nearly double by the year 2030 as the rate of new diagnoses accelerates.
- Diabetes is the most expensive chronic condition in the United States–costing $412.9 billion in 2022–and is the eighth leading cause of death. One in four healthcare dollars spent in America goes to treating diabetic patients.
- Diabetes has a disproportionate impact on low-income individuals and certain racial and ethnic groups, including American Indians, Alaskan Natives, and Black and Hispanic people.
- Investment in digital diabetes management solutions has been significant. Since 2010, $5.7 billion of venture capital has been invested in companies providing these solutions, and transactions (including mergers and acquisitions and other investments) have totaled $58 billion.
- Purchasers (i.e., health plans, self-insured employers, and providers) have responded by widely adopting these solutions because, if they work well, people live healthier, longer lives and require less costly medical care. However, purchasers would benefit from deeper analysis of clinical and economic impact and clear information on performance expectations.
- Effective digital diabetes tools should demonstrate substantial and durable progress toward glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes, resulting in a lower prevalence of uncontrolled type 2 diabetes across the population. This would result in important reductions in diabetes-related health risks, fewer prescriptions, fewer healthcare events, and lower healthcare spending.
- Digital solutions should target patients with severe disease and diverse groups who would benefit most from improved self-management support. Ideally solutions should be aiming to help patients achieve diabetes remission.
Additional resources
October 2023
Assessment Area BriefAssessment area brief for PHTI’s assessment of non-continuous glucose monitoring solutions associated with a mobile or web application to guide therapeutic workflows.
October 2023
Diabetes Remote Patient Monitoring Methodology Overview (Presentation with Audio)A review of PHTI protocol for systematic literature review of clinical impact.
October 2023
Systematic literature review of remote patient monitoring among patients with type II diabetesInternational prospective register of system reviews (PROSPERO), National Institute for Health and Care Research
Contact
Get in touch with us if you want to learn more about opportunities to provide input on this assessment.
"*" indicates required fields
Read an overview of our assessment Approach and Framework
view assessment frameworkRelated news & resources
-
Mar 21, 2024Announcement
New Report Finds That Digital Diabetes Management Tools Fail to Deliver Meaningful Health Benefits to Patients While Increasing Spending
Independent evaluation from Peterson Health Technology Institute recommends new directions for digital diabetes solutions
-
Read ArticleMar 21, 2024News Coverage
Forbes
Diabetes Monitoring Apps Don’t Deliver Meaningful Benefits, Report Says
-
Read ArticleMar 21, 2024News Coverage
STAT
Digital tools for diabetes management did not deliver benefits that justify cost, new report finds
-
Read ArticleMar 21, 2024News Coverage
Modern Healthcare
Study: Digital diabetes tools not worth the cost
-
Read ArticleMar 25, 2024News Coverage
Fierce Healthcare
Diabetes management tools not worth the cost, study finds
-
Read ArticleMar 24, 2024News Coverage
MedCity News
Report: Digital Diabetes Management Tools Fall Short
Stay up to date
Sign up to receive updates.
Fill out the details below to download the report:
"*" indicates required fields